QuamM
Qualification of magnetic materials for additive manufacturing
This project was honoured with the Award for Sustainability and Interdisciplinarity at TU Darmstadt, which was offered by the Vereinigung der Freunde der TU Darmstadt.
Summary
Period:1.2021 – 12.2022
---
Prof. Dr. Oliver Gutfleisch
Fachgebiet für Funktionale Materialien (FM), FB 11
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Matthias Weigold
Institut für Produktionsmanagement, Technologie und Werkzeugmaschinen (PTW), FB 16
---
Project description:
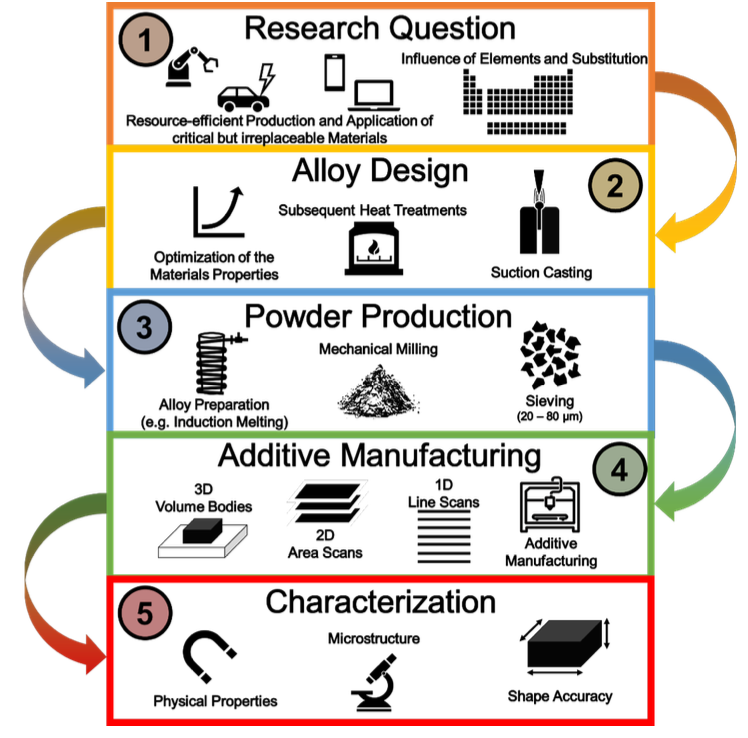
The Corona pandemic since 2020 and the Russia sanctions since 2022 have highlighted the global dependencies on supply chains and raw materials. In addition, society's desire for sustainable products is growing. At the same time, new manufacturing routes are opening up new opportunities to address these challenges. Within the QuamM project, the potentials and challenges of additive manufacturing for the resource-efficient processing of magnetic materials were therefore investigated.
For this purpose, different alloy designs were developed and the basic suitability was tested in an analogue process (suction casting) or the alloy design was adapted according to the requirements. If the suitability was positive, small quantities of powder (<50 g) were produced by mechanical milling and made available for additive manufacturing. Laser-based powder bed melting (PBF-LB) was used as the additive manufacturing process. Test specimens were produced by iteratively varying the process parameters. The target parameters for qualification were initially the uniformity of the process and the density of the solid bodies. Through new findings within the project, the evaporation of important alloying elements, crack formation and reduced imaging accuracy were identified as challenges. While the latter influence the basic manufacturability, the evaporation of alloying elements leads to altered microstructure characteristics and must be taken into account accordingly in the alloy design. Through this methodical procedure, three different alloys with promising properties could be qualified. The exploitation of material potentials through targeted microstructure adjustment represents a long-term possibility for the efficient use of resources, which has been placed in further research applications.
Publications
Schäfer, Lukas et al.; “Design and Qualification of Pr–Fe–Cu–B Alloys for the Additive Manufacturing of Permanent Magnets.” Advanced Functional Materials 31.33 (2021): 2102148
Julian Storch, Entwicklung einer Methode zur Materialqualifizierung von magnetischen Materialien hergestellt durch pulverbettbasiertes Laserschmelzen
Shen, Shangbing; “Ce(CoxCu1-x)5 magnets: from single crystals to selective laser melted alloys”
Harbig, Jana et al. “Efficient Material Qualification Process for Laser Powder Bed Fusion of Metals” Journalbeitrag in “Additive Manufacturing Letters”, Begutachtungsprozess